RAM (Random access memory)
Most FPGAs include specific blocks dedicated to implement RAMs in an optimal way. These are not special LUTs, but directly RAMs that can be used if the VHDL is written correctly.
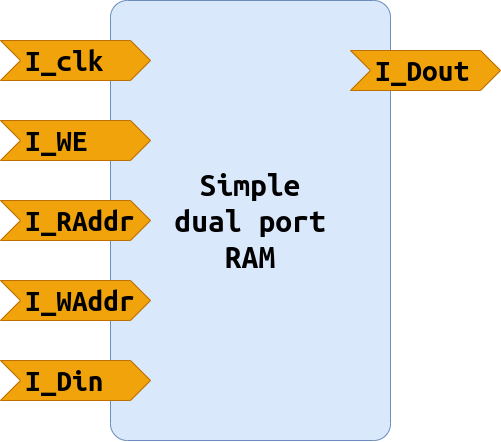
Simple dual port RAM
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37 library ieee ;
use ieee.std_logic_1164. all ;
use ieee.numeric_std. all ;
entity GenericMemorySimpleDualPort is
generic (
G_AddressWidth : integer := 6 ;
G_WordLength : integer := 16
);
port (
I_Clk : in std_logic ;
I_We : in std_logic ;
I_AddrRead : in std_logic_vector ( G_AddressWidth - 1 downto 0 );
I_AddrWrite : in std_logic_vector ( G_AddressWidth - 1 downto 0 );
I_Din : in std_logic_vector ( G_WordLength - 1 downto 0 );
O_Dout : out std_logic_vector ( G_WordLength - 1 downto 0 )
);
end GenericMemorySimpleDualPort ;
architecture archi_GenericMemorySimpleDualPort of GenericMemorySimpleDualPort is
type RamType is array ( 0 to 2 ** G_AddressWidth - 1 ) of std_logic_vector ( G_WordLength - 1 downto 0 );
signal RAM : RamType ;
begin
process ( I_Clk )
begin
if rising_edge ( I_Clk ) then
if I_We = '1' then
RAM ( to_integer ( unsigned ( I_AddrWrite ))) <= I_Din ;
end if ;
O_Dout <= RAM ( to_integer ( unsigned ( I_AddrRead )));
end if ;
end process ;
end archi_GenericMemorySimpleDualPort ;
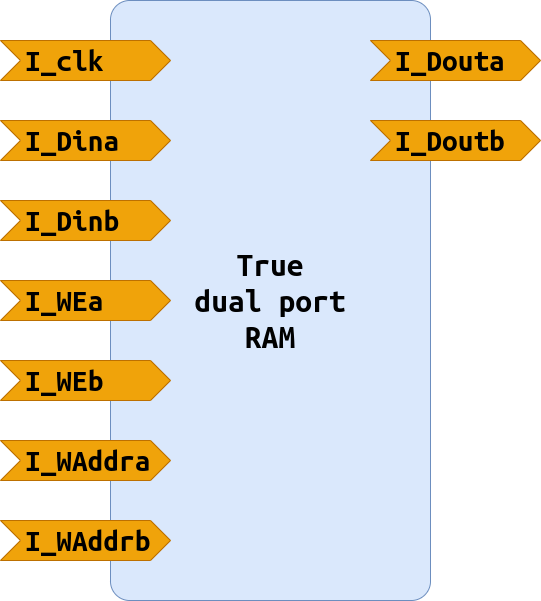
True dual port RAM
work in progress
Fill RAM content at declaration
work in progress
From the VHDL code
work in progress
From a text file
work in progress
See section
Example of RAM VHDL description infered on block RAM