Finite State Machine (FSM)
Even at a relatively low level of complexity, a circuit is often divided into several main blocks. Most of the time an operative unit, containing all the arithmetic operators, processing units etc, and a control part, implemented with a Finite State Machine (FSM).
FSM constitutive functions
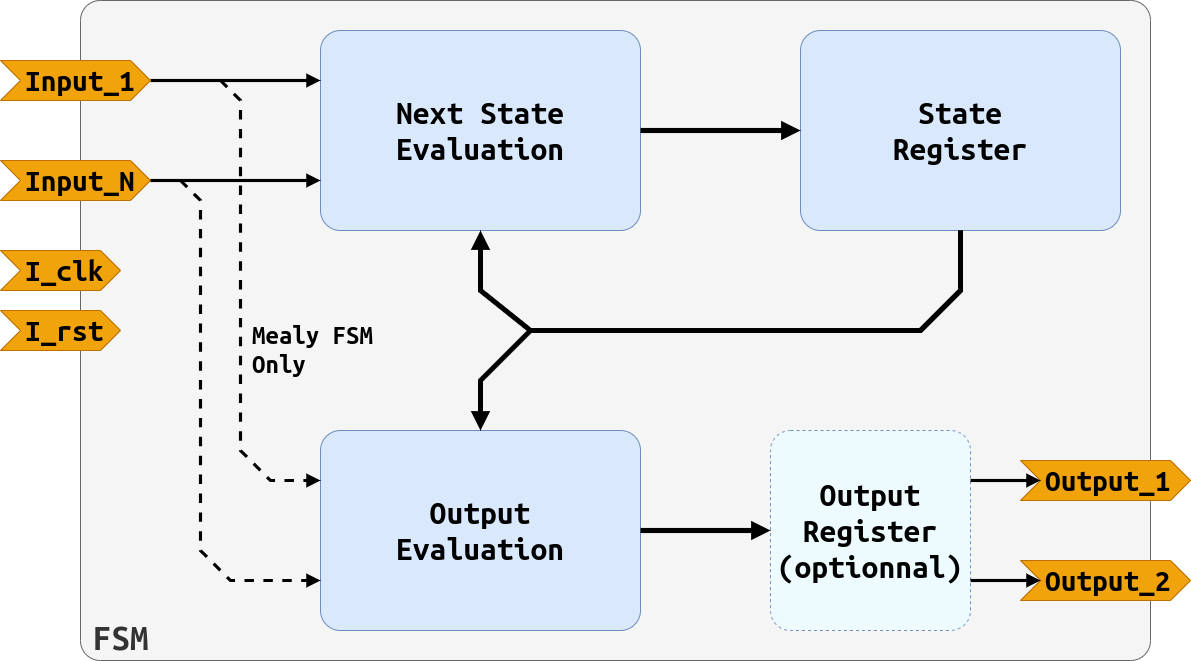
A FSM has three functions (as seen in the figure below):
- Indicate what state the system is in (State Register)
- evaluate what will be the future state of the system according to the present state and the values of the inputs (Next State Evaluation)
- drive the control signals of the operative part and, if necessary, of the system's outputs according to the present and eventually states of the inputs (Output Evaluation)
Note
Those three functions have to be describe in VHDL. They can be described with one process for each, or regroup into one process only, and everything in between.
FSM types
We distinguish two types of FSM:
- Moore's FSM whose output signals depend only on the present state
- Mealy's machines whose output signals depend on the present and input states.
The Mealy machines have the advantage of being more reactive because we can make the output signals evolve not only according to the present state, but also according to the inputs, thus on the transitions between states. Speaking of output signals, they can be synchronized or not. If they are not synchronized, the FSM will be more reactive, but will introduce a longer logic path, thus potentially a lower operating frequency. If they are, the FSM will be less reactive, but will be better in terms of achievable frequency.
|
Moore |
Mealy |
| Asynchronous outputs |
1 cycle response time, Low frequency |
0 cycle response time, Low frequency |
| Synchronous outputs |
2 cycle response time, High frequency |
1 cycle response time, High frequency |

VHDL descriptions
Three process way
Regarding the previous architecture, the most intuitive way of describing a FSM in VHDL is to use three processes :
- The first one is a synchronous process used to update the present state register with the value of the futur state
- The second one is a combinatorial process used to compute the futur state based on the present state and the inputs
- The third one is also a combinatorial process used to compute the values of the outputs based on the present state alone in the case of a Moore FSM, or on the present state and the inputs in the case of a Mealy FSM
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152 | library ieee;
use ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
use ieee.numeric_std.all;
entity fsm is
port (
I_Clock : in std_logic;
I_reset : in std_logic;
I_1 : in std_logic;
I_2 : in std_logic;
I_3 : in std_logic;
I_4 : in std_logic;
I_5 : in std_logic;
O_1 : out std_logic;
O_2 : out std_logic;
O_3 : out std_logic;
O_4 : out std_logic
);
end entity fsm;
architecture a_fsm of fsm is
type T_State is (ST0, ST1, ST2, ST3, ST4, ST5, ST6, ST7);
signal SR_present : T_State;
signal SC_futur : T_State;
begin
process(I_Clock, I_reset) is
begin
if I_reset = '1' then
SR_present <= ST0;
elsif(rising_edge(I_Clock)) then
SR_present <= SC_futur;
end if;
end process;
process(SR_present, I_1, I_2, I_3, I_4, I_5)
begin
case SR_present is
when ST0 =>
SC_futur <= ST1;
when ST1 =>
if(I_1 = '1')then --Cond1
SC_futur <= ST2;
else
SC_futur <= ST1;
end if;
when ST2 =>
if(I_2 = '1' and I_4 = '0')then --Cond2
SC_futur <= ST3;
else
SC_futur <= ST2;
end if;
when ST3 =>
if(I_3 = '1')then --Cond3
SC_futur <= ST4;
elsif(I_2 = '1')then --Cond4
SC_futur <= ST6;
else
SC_futur <= ST3;
end if;
when ST4 =>
if(I_1 = '0' and I_2 = '1')then --Cond5
SC_futur <= ST5;
elsif(I_5 = '1')then
SC_futur <= ST7;
else
SC_futur <= ST4;
end if;
when ST5 =>
if(I_5 = '1')then --Cond8
SC_futur <= ST3;
else
SC_futur <= ST5;
end if;
when ST6 =>
if(I_4 = '1' and not (I_2 = '1' xor I_3 = '0'))then --Cond7
SC_futur <= ST1;
else
SC_futur <= ST6;
end if;
when ST7 =>
SC_futur <= ST7;
when others =>
SC_futur <= ST0;
end case;
end process;
process(SR_present, I_1, I_2, I_3, I_4, I_5)
begin
-- default output values
O_1 <= '0';
O_2 <= '0';
O_3 <= '0';
O_4 <= '0';
case SR_present is
when ST2 =>
O_1 <= '1'; --moore output (depending on state only)
if(I_2 = '1' and I_4 = '0')then --Cond2
O_2 <= '1'; --mealy output (depending on state and input)
else
O_2 <= '0'; --mealy output (depending on state and input)
end if;
when ST3 =>
O_1 <= '1';
O_3 <= '1';
when ST4 =>
O_2 <= '1';
O_3 <= '1';
if(I_1 = '0' and I_2 = '1')then --Cond5
O_4 <= '1';
else
O_4 <= '0';
end if;
when ST5 =>
O_1 <= '1';
when ST6 =>
O_1 <= '1';
if(I_4 = '1' and not (I_2 = '1' xor I_3 = '0'))then --Cond7
O_2 <= '1';
else
O_2 <= '0';
end if;
when ST7 =>
SR_present <= ST7;
when others =>
SR_present <= ST0;
end case;
end process;
end a_fsm;
|
The last process, managing the outputs, can be split in several explicit or implicit processes for more convenience.
Two process way
One synchronous process way
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113 | library ieee;
use ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
use ieee.numeric_std.all;
entity fsm is
port (
I_Clock : in std_logic;
I_reset : in std_logic;
I_1 : in std_logic;
I_2 : in std_logic;
I_3 : in std_logic;
I_4 : in std_logic;
I_5 : in std_logic;
O_1 : out std_logic;
O_2 : out std_logic;
O_3 : out std_logic;
O_4 : out std_logic);
end entity fsm;
architecture a_fsm of fsm is
type T_State is (ST0, ST1, ST2, ST3, ST4, ST5, ST6, ST7);
signal SR_present : T_State;
begin
process (I_Clock, I_reset) is
begin
if I_reset = '1' then
O_1 <= '0';
O_2 <= '0';
O_3 <= '0';
O_4 <= '0';
SR_present <= ST0;
elsif(rising_edge(I_Clock)) then
case SR_present is
when ST0 =>
SR_present <= ST1;
when ST1 =>
if(I_1 = '1')then --Cond1
SR_present <= ST2;
else
SR_present <= ST1;
end if;
when ST2 =>
O_1 <= '1'; --moore output (depending on state only)
if(I_2 = '1' and I_4 = '0')then --Cond2
SR_present <= ST3;
O_2 <= '1'; --mealy output (depending on state and input)
else
SR_present <= ST2;
O_2 <= '0'; --mealy output (depending on state and input)
end if;
when ST3 =>
O_1 <= '1';
O_3 <= '1';
if(I_3 = '1')then --Cond3
SR_present <= ST4;
elsif(I_2 = '1')then --Cond4
SR_present <= ST6;
else
SR_present <= ST3;
end if;
when ST4 =>
O_2 <= '1';
O_3 <= '1';
if(I_1 = '0' and I_2 = '1')then --Cond5
SR_present <= ST5;
O_4 <= '1';
elsif(I_5 = '1')then
SR_present <= ST7;
O_4 <= '0';
else
SR_present <= ST4;
O_4 <= '0';
end if;
when ST5 =>
O_1 <= '1';
if(I_5 = '1')then --Cond8
SR_present <= ST3;
else
SR_present <= ST5;
end if;
when ST6 =>
O_1 <= '1';
if(I_4 = '1' and not (I_2 = '1' xor I_3 = '0'))then --Cond7
SR_present <= ST1;
O_2 <= '1';
else
SR_present <= ST6;
O_2 <= '0';
end if;
when ST7 =>
SR_present <= ST7;
O_1 <= '1';
O_2 <= '1';
O_3 <= '1';
when others =>
SR_present <= ST0;
end case;
end if;
end process;
end architecture a_fsm;
|

